Building Leader Character
This blog was written by Maureen Metcalf, based on the article Developing Leadership Character by Mary Crossan, Gerard Seijts, and Jeffrey Gandz, published in the Ivey Business Journal Issues: January / February 2012. It is a companion to the International Leadership Association Interview Series podcast Leader Character.
Leadership character is critical in our rapidly changing world, filled with disruption and ethical challenges. According to the article, Developing Leadership Character, “When it comes to leadership, competencies determine what a person can do. Commitment determines what they want to do, and character determines what they will do.”
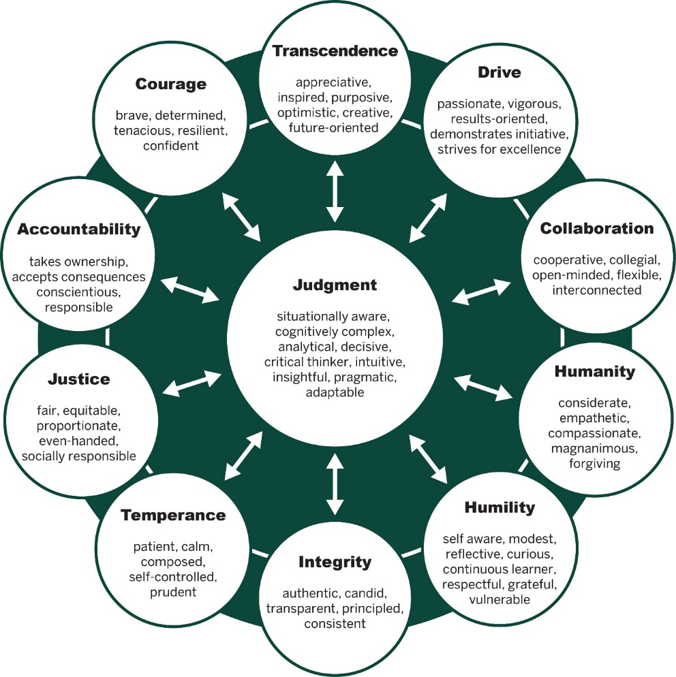
“Character fundamentally shapes how we engage the world around us, what we notice, what we reinforce, who we engage in conversation, what we value, what we choose to act on, how we decide…and the list goes on.” While there is no generally accepted definition of character, Mary Crossan and her co-authors focus on personality traits, values, and virtues as the focus of virtue-based character in their article, Developing Leader Character. They also highlight the importance of Judgment, which is at the center of their leader character framework shown in Figure 1.”
All behaviors associated with character are virtuous, meaning that they have been vetted by research as desirable by cultures throughout history. And because only a few of the behaviors are trait-based, character can be developed. Some behaviors can be viewed as values, but it is essential to recognize that they are not just any values but only ones that satisfy the criteria of being virtuous. The Developing Leadership Character article analyzes eleven leadership virtues and what happens when they are either lacking or over weighted. Aristotle noted that any virtue will operate like a vice when other virtues do not support it. Thus, Courage becomes recklessness when not supported by Temperance. Integrity not supported by Humanity and Humility runs the risk of a person being dogmatic and egotistic. The aim is for individuals to develop strength in all dimensions of character. The following example from their article describes how virtue can strengthen an individual’s performance and become a vice when not supported by other character dimensions.
- Accountability ensures that leaders own and commit to their decisions and encourages the same in others.
- Without Accountability, leaders don’t commit to or own their decisions and cannot get others to do so. They blame others for poor outcomes and, in doing so, create a culture of fear and disengagement. People stop caring, with potentially disastrous consequences.
How do we develop character?
Because character is a habit, the question is, “Who am I becoming while I am busy doing?” advises Crossan. We are always becoming something – more courageous, less courageous, more humble, or less humble. Developing character requires understanding what it is, mainly how virtues could operate like a vice. Many people are proud of their candor, their modesty, their calm, etc., but if these behaviors and the dimensions of character they support are not part of a strong network of behaviors, there is every possibility that they are counterproductive – operating like a vice. Consider something like “grit,” widely touted as necessary. Many behaviors within Courage and Drive are grit-like, but research on grit has shown that it can lead to burnout. Why? Because you need the other dimensions of character, particularly Judgment, to know when to exercise grit and when not to.
Developing character flies in the face of many approaches to leadership that suggest we should focus on our strengths and rely on others to complement our weaknesses. Complementarity makes sense for personality traits like introversion or extroversion, but weaknesses compromise individual judgment when it comes to character.
In another article co-authored by Mary Crossan, Elevating Leader Character Alongside Competence in Selection, “Character is constantly evolving, both personally and professionally. Thus, a person’s work and life experiences fundamentally shape character, and the story about who someone is and why they have become the person they are is unique to each person.” It will be necessary for the individual and the organization to attend to the virtues they want to see and understand how different virtues complement one another and how they complement one another.
We are unlikely to change character elements for each item referenced above if we are not conscious and motivated. Self-awareness, conscious choice, rewarding context, aligning complementary virtues, practicing virtuous behaviors, and motivation all impact the choice and outcome of the work to build character.
As we wrap up the discussion, I would like to return to the article Mary Crossan and her colleagues wrote, “Character is not something that you have or don’t have. All of us have character, but the key is the depth of development of each facet of character that enables us to lead holistically. Character is not a light switch that can be turned on and off. There are degrees, and every situation presents a different experience and opportunity to learn and deepen character. In particular, and for better or for worse, character comes to the fore when managing a crisis. No one is perfect when it comes to character. Given that its development is a lifelong journey, we will rise to the occasion in some situations and disappoint ourselves and those around us in others.”
In our current, fast-changing environment, we need leaders who demonstrate character, informed by leadership virtues. Organizations must understand how to build character and the contexts that inhibit character development.
About the Author
Maureen Metcalf, CEO of the Innovative Leadership Institute, is a renowned executive advisor, coach, consultant, author, and speaker.



Trackbacks & Pingbacks
[…] style can be beneficial. Sometimes, when employees are panicked, they need the guidance of a strong and confident leader. However, more often than not, autocratic leadership isn’t as beneficial as it […]
[…] style can be beneficial. Sometimes, when employees are panicked, they need the guidance of a strong and confident leader. However, more often than not, autocratic leadership isn’t as beneficial as it […]
Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!