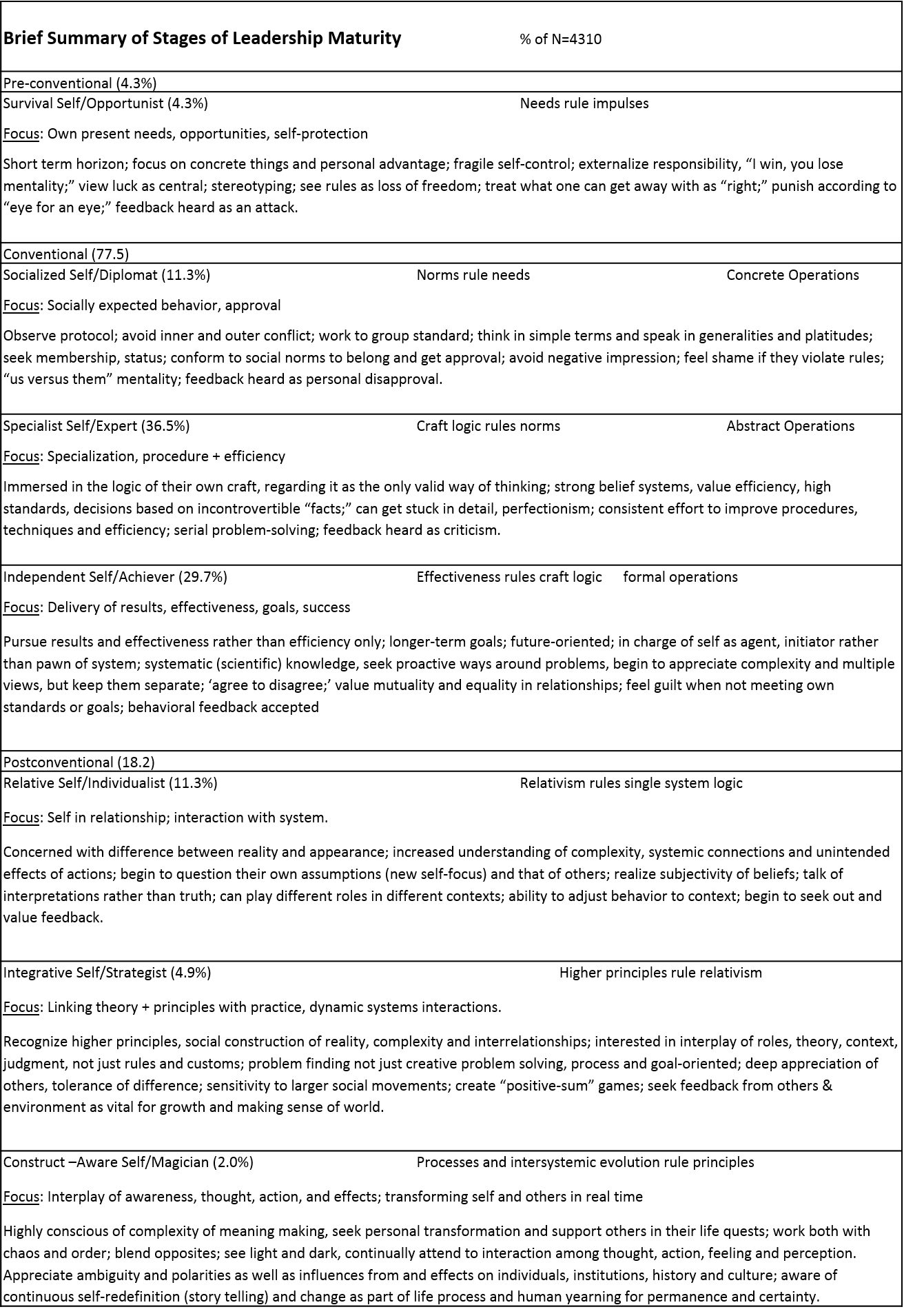
Organizations Have Personality Types: How Do You Fit?
 This guest blog was written as a companion to the podcast with Belinda Gore, Building Leadership Self-Awareness Using Personality Type. In the interview and the blog, Belinda explores how she uses the Enneagram to help leaders build the self-awareness that enables them to perform effectively.
This guest blog was written as a companion to the podcast with Belinda Gore, Building Leadership Self-Awareness Using Personality Type. In the interview and the blog, Belinda explores how she uses the Enneagram to help leaders build the self-awareness that enables them to perform effectively.
As a reminder from a prior post, when the 65-member Advisory Council for the Stanford Graduate School of Business was polled several years ago on the topic of what is most important to include in the school’s curriculum, there was overwhelming agreement that the most important thing business school graduates needed to learn was self-awareness and the resulting ability to reduce denial in their perceptions of themselves and their actions. Pretty impressive. This speaks to the emerging recognition that we highlight in Innovative Leadership: leaders can derail the most progressive initiatives toward an organization’s sustainable success through their personality quirks and biases.
In my experience using the Enneagram system as a psychologist and a leadership coach over the past twenty-three years, I find the Enneagram to be more robust than any other system I have encountered. Many organizations are familiar with DISC, MBTI, Social Styles, and other systems, and training in these models has given employees at every level of the organization a foundation in models for self-awareness. I have found leaders at every level able to learn the rich and versatile information the Enneagram offers readily.
Just as leaders have “personalities,” so do organizations. This is just another way to think about the organizational culture, the mission or role the organization seeks to fulfill, the favored strategies for accomplishing goals, the behaviors that are rewarded and those that are not, and the subtle hiring filters that tend to screen out people who do not fit. The senior leaders of the organization may or may not reflect the culture. It is immensely valuable for leaders to determine their organization’s personality type to harness the natural strengths of that pattern and avoid the embedded tendencies that create problems. Leaders are likely to have a strong influence on the development of organizational culture, but without clear awareness, they may not realize how the leader and the group are aligned and how they sometimes work in opposition.
For example, a mid-size utility company instituted leadership development training based on the Enneagram. In assessing several hundred people within the company, it became clear that the organization has a Type Six culture of loyalty. The Type Six pattern is reflected in the company’s mission to provide reliable and affordable gas and electric energy to their customers and to promote safety for their employees in power plants and distribution. Loyalty is highly valued within the company; many employees have worked there for twenty years or more. Attention is paid to identifying potential problems and working out solutions before they occur; when there is a power outage due to weather conditions, there is an expectation that the entire workforce will be available to provide support until the situation is resolved. In some Enneagram training groups of individual contributors, up to 50% of the employees determined for themselves—using an assessment tool along with classroom training and guided group discussion—to have a Type Six personality. Among mid-level managers, that percentage drops to around 35%, and in the top group of senior leaders, less than 10% assess themselves as having a Type Six personality pattern.
This is not unusual. Why? Because leaders in the C-suites, those who have risen to the top leadership levels, are not equally distributed around the Enneagram circle but tend to cluster in another sub-grouping.
As a leader, you must understand your type to build awareness of your predispositions. It is also important to understand the organization’s type to understand better how you fit within it. Understanding your type will lead you to the following questions:
- Is your style a natural fit with that of the majority?
- What gifts do you bring because of your similarities?
- What blind spots exist if too many people share the same personality type?
- If you have a different type, how do your predispositions fill gaps?
- How do you manage your similarities and differences to fit and fill gaps?
By answering these questions, you will have a clearer sense of how you, as a leader, may best contribute and some of the inherent struggles if you have a different type than the majority that comprises the culture. While being part of the minority allows you to fill gaps, you may also find yourself excluded or struggling to communicate effectively. Through self-awareness and skillful interactions, you will be able to navigate any organization’s predispositions.
About the Author
Belinda Gore, PhD focuses on designing, developing, and delivering leadership, assessments, workshops, and coaching. She is a key thought leader in developing the Innovative Leadership framework. She is a psychologist, executive coach, and experienced seminar leader skilled in supporting her clients in high-level learning. With 30 years’ experience in leadership development and interpersonal skills training, she is known for helping teams discover strength in their diversity to achieve their mutual goals, and works with individual leaders to access their natural talents to maximize effectiveness and personal satisfaction. Her clients have included senior leadership in global companies, senior and middle management in corporate and nonprofit organizations, and entrepreneurs. She will lead our new service line, which is focused on helping leaders and their organizations build resilience and offering leadership team development, board development, coaching, and Enneagram assessment.

 This blog is a companion to the interview with Terri O’Fallon. What is A Level 5 / Teal Organization? Terri O’Fallon, PhD, wrote this post.
This blog is a companion to the interview with Terri O’Fallon. What is A Level 5 / Teal Organization? Terri O’Fallon, PhD, wrote this post.